Skin Cancer Removal
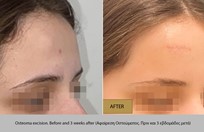
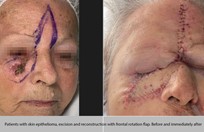
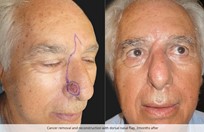
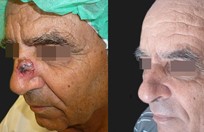
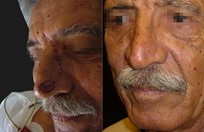
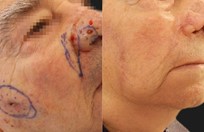
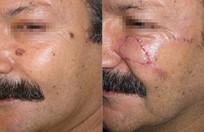
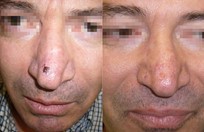
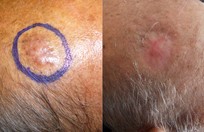
More than 25% of the total population will get a skin cancer in their lifetime. Almost all skin cancers are caused by sunburns. Aging people should also not burn as the damage caused by ultraviolet light is not as well reversed by DNA repair enzymes. This is why no one should sunburn anymore. The longer you wait to have a skin cancer removed, the bigger it gets, and the more complicated the reconstruction becomes
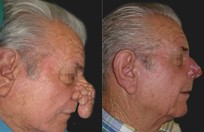
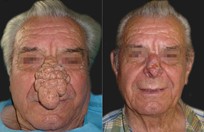
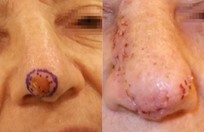
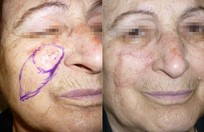
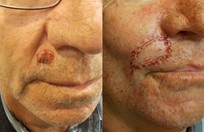
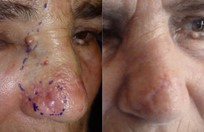
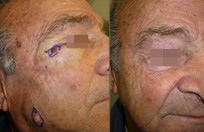
Basal cell skin cancer is the most common kind of skin cancer. It is usually a smooth pink or red flat or lumpy area. Basal skin cancer does not go away but gradually gets larger. These cancers do not tend to grow deeply and usually what you see is what you've got. The cure rate with removing these surgically is over 95%.
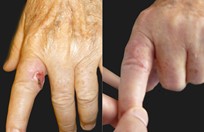
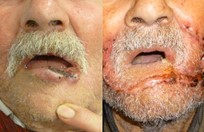
Squamous cell skin cancer is very much the same as basal cell skin cancers in appearance except the red areas tend to have hard rough spots on them and bleed more easily. Squamous cell skin cancers also have a slightly higher risk of metastasizing than basal cell skin cancers.
Squamous cell skin cancers on the penis, anal area or labia minora/majora, vagina, extract usually from HPV (Human Papilloma Virus), that’s why have to be removed immediately by laser (laser HPV removal).
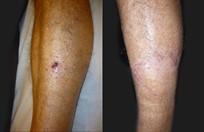
Malignant melanoma occurs in 1% of the population. There are three things that make melanoma obvious, as this is not a subtle skin cancer in most instances: 1) Melanoma is usually black or has black in it, and arises from moles 1/3 of the time. 2) Melanoma tends to grow quickly and will often double in size over weeks. 3) Melanoma tends to have an unusual shape, as opposed to benign moles which are usually round or oval.